the prominent transmission function is the transmission of rotation from the engine to the conductive wheels and adjusting the transmission number. The standard transmission includes gearbox, gearbox, as well as cardan transmission.
When moving along a straight system, it is enough - the wheel rotation is carried out in one speed range. But when performing styles, the wheels move on different radii, passing different distances. Accordingly, some of them can book. This effect also increases the load on the components of the transmission, increases the risk of damage to the drive elements.
To prevent this from happening, a differential node is added to the transmission. Speaking in plain language, how it works differential , it slows down the inner wheels and accelerates external. This eliminates the pilgrimage and other negative effects of this effect.
Basic varieties of differential nodes
Differentials are classified into 2 types based on the place of installation:
- intercostal;
- Amount.
The first type is used on vehicles with one conductive axis. On the rear -wheel drive machines, the differential is mounted on the gearbox. In front -wheel drive transport, the differential is connected directly to the checkpoint.
only -wheelchair transport is completed. It provides the optimal distribution of rotation between the axes when moving on the road with an uneven surface. All -wheel vehicles usually use a combination from different differential units.
Features of the functioning of the node
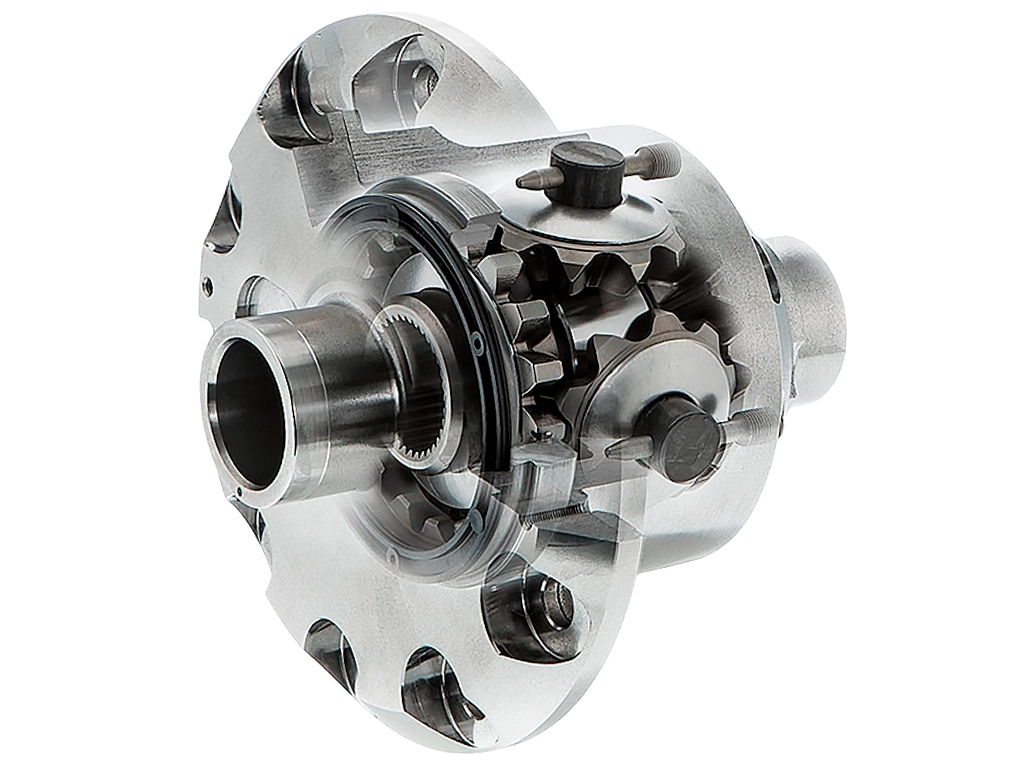
Differentials are made on the basis of a planetary gearbox. They consist of a gear of conductive and driven types, satellites and housing.

driven gears are with the same or different number of teeth. The former are called symmetrical, due to the proportional distribution of rotation between the shafts. The second (asymmetrical) performs the distribution by a given value.
symmetrical gears are installed on intercostal differentials, asymmetrical - on the inter -axis.
Differential Operation:
- On a direct trajectory of motion, all wheels receive identical resistance from the road. The rotation from the checkpoint is fed to the main wheel of the gearbox. In parallel with it, the housing of the differential node is rotated. The satellites convey the torque to the gear -type gear in identical ratio, remaining fixed with respect to their own axes.
- The interior wheels undergo more resistance during rotation. Because of this, the driven gear slows down, and the satellites begin to rotate on the axes. The motion of satellites contributes to the growth of rotation speed of the outer wheel.
Due to the differential, the total torque does not change, but is evenly distributed between the wheels.
Differential lock
Differential has a significant drawback. If the resistance on a wheel disappears, then there is a sharp jump in the angular speed. As a result of rotation, only this wheel is fed. Because of this, the second wheel stops. As a result - the machine is discharged.
To eliminate this problem, it is necessary to slow down the whispering wheel. To do this, the lock is used.
How does differential lock work? The complete involves the rigid connection of the differential body and one of the half. The differential simply cannot spin the gear gear faster. This eliminates the redistribution of rotation.
Partial lock systems limit the effort that can be transmitted between the nodes.
Lock management
lock is actively used in the inter -axial and intercostal differential. It can be activated in automatic or manual mode.

Manual differential lock - how does it work? It is used only as needed. The driver chooses himself when to turn on the actuator, which provides a rigid joint of the elements of the differential unit with each other.
blocking drives are classified into electromechanical and mechanized, as well as pneumatic and hydraulic.
Manual management involves compliance with certain rules, knowledge of how the blockage of the intercostal differential works. If you forget to turn off the differential lock and continue traffic with good connection of both road wheels, there is a risk of transmission damage.
Automatic differentials
systems of this type are called self -wing. They are characterized by the fact that the lock is made without the direct involvement of the driver.
How does the differential work? The simplest solution involves the presence of a package of disks. Some disks are rigidly connected to the differential body, others - with the axis. They are also tightly pressed.
In normal mode, the disc package rotates with the differential. When the angular velocity grows, some of the disks begin to rotate faster. But due to friction, the growth of the angular velocity slows down.
The electronic blocking of the inter -pial differential is the principle of operation. Only here instead of disks is used ABS. If one of the wheels increases the angular velocity, the brake system automatically slows it.